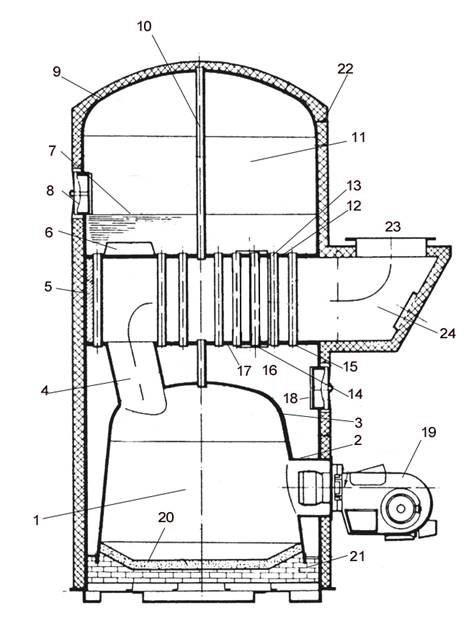
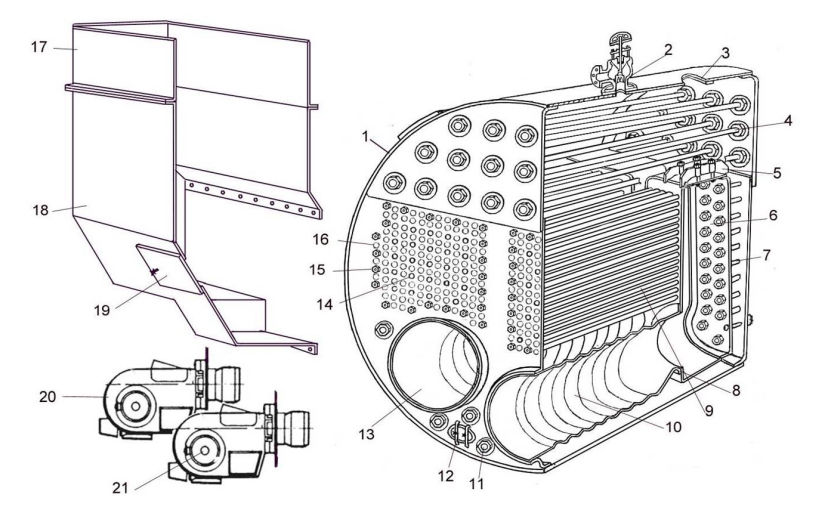
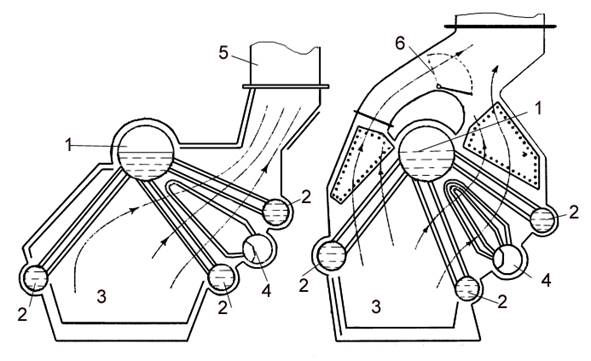
Căldarea auxiliară verticală (fig. 1)
1. Focar
2. Tub de foc
3. Coroana focarului
4. Eşapament eliptic
5. Placă de ancorare
6. Traversă principală
7. Nivelul normal de apă
8. Gură de vizită
9. Coroana anvelopei
10. Tirant central
11. Cameră apă abur
12. Placă tubulară superioară
13. Tuburi ordinare
14. Tuburi coborâtoare
15. Tuburi tirante
16. Camera de apă
17. Placa tubulară inferioară
18. Guri de vizită
19. Arzător de combustibil
20. Izolaţie refractară
21. Zidăria vetrei
22. Izolaţie
23. Canal vertical de gaze de ardere
24. Cutia/camera de fum